
In this AI Era, laptops are equipped with any type of processor. You might be considering that one of them will be based on your budget but that is not necessarily so. There are other factors to be considered as far as its base count and clock speeds are concerned to your workload requirements.
Today we will discuss AMD Ryzen 7 7730U vs Intel Core i5 13420H two of the most popular processors that are used in the modern laptops to code and programme.
AMD Ryzen 7 7730U vs Intel Core i5 13420H: Which is the Best to use in Coding?
We perform objective and data analysis on all processors we compare. There are various individual data points that are recorded and analysed in each processor.
The following comparison chart compares the key performance measures of each category with respect to the specifications and actual performance that we have reviewed so far.
This is AMD Ryzen 7 7730U vs Intel Core i5 13420H, but we have taken into account how these processors can be used in different coding and programming situations. These typically include code compilation, running of virtual machines, or managing multiple development environments at the same time.
What Is AMD Ryzen 7 7730U?
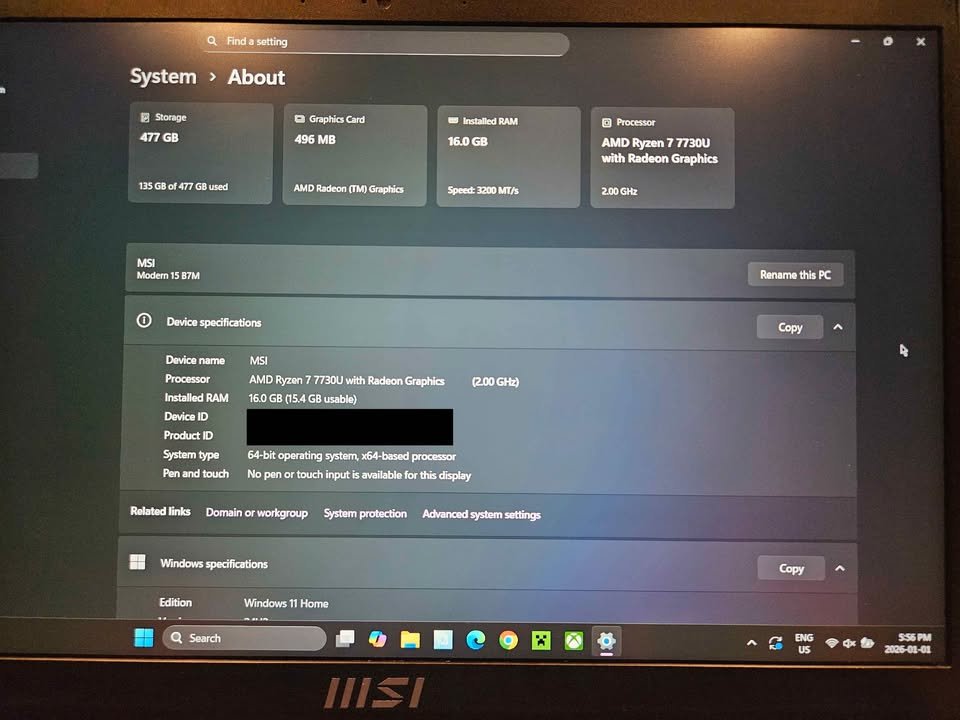
We can begin with AMD Ryzen 7 7730U, a mobile processor that is based on the Zen 3 architecture. This chip was made in high-end laptops and was launched in Q1 2023. AMD came up with it to provide good battery life and efficient multitasking performance.
The Ryzen 7 7730U is a successful product among developers and the successor of the AMD Barcelo. The difference is that it has an 8-core, 16-thread design with a low-power 15W TDP design.

This processor is very popular in different segments of laptops today. Ultrabooks, business laptops, creator notebooks, and dozens of other devices that run on the Ryzen 7 7730U can be purchased by consumers.
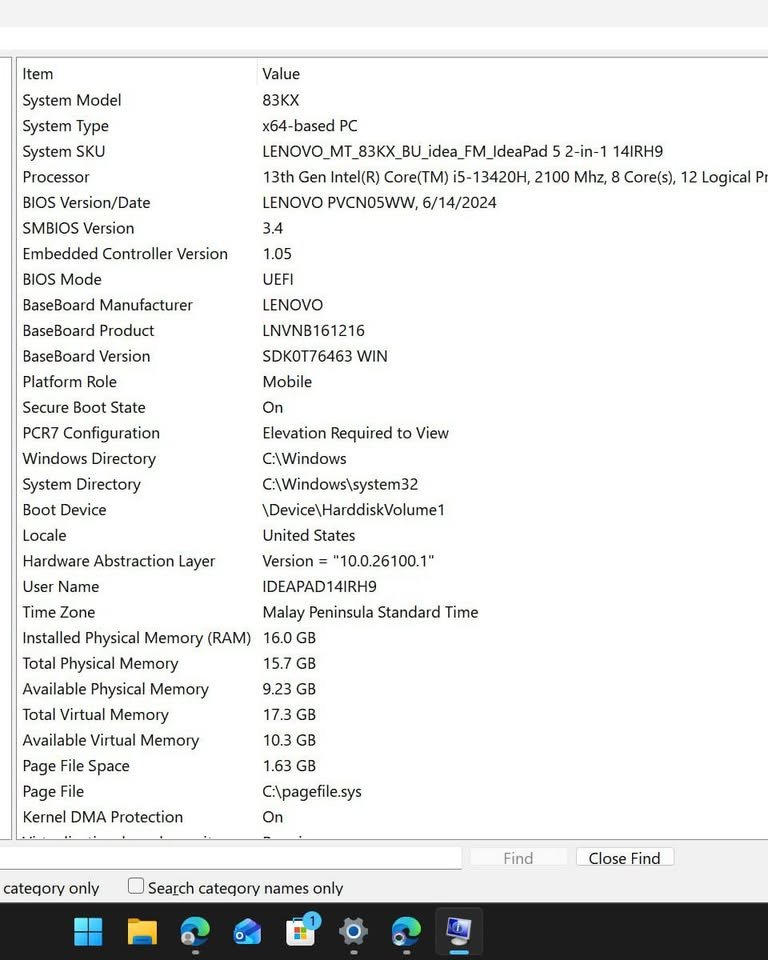
The base clock of 2 GHz, which is lower than the other development environments, may be a concern to you should you be working with a demanding development environment, a trade-off with efficiency.
Nevertheless, high-end laptops using this processor can increase to 4.5 GHz on demand. Manufacturers normally accompany it with sufficient cooling solutions. To top it all, the 16MB L3 cache is used to sustain the smooth performance even in the case of intensive coding.
We do not need to elaborate on this one, but the Ryzen 7 7730U is based on the 7nm FinFET process technology of TSMC. There is also all you would want in a modern development work inside, such as AVX2, SSE4.2, and other instruction set extensions support.
What Is Intel Core i5 13420H?
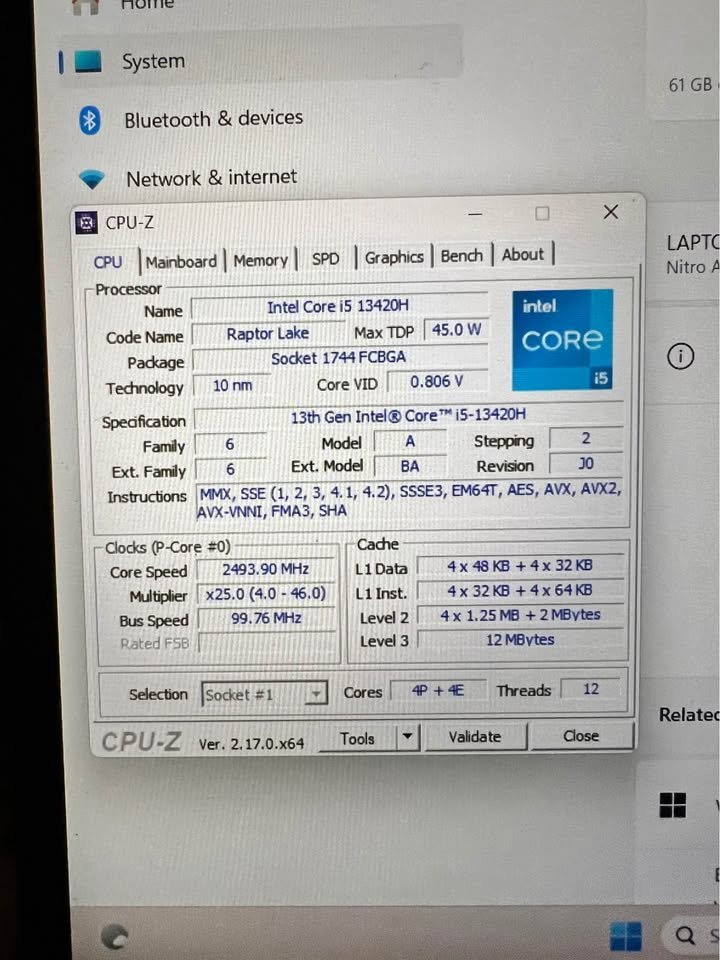
Intel Core i5 13420H is a strong mobile processor that is based on the hybrid architecture of Intel. It is made with Intel 7 lithography and is a combination of Performance-cores and Efficient-cores. This processor became a member of the 13th Gen Raptor Lake family after Intel switched to the hybrid design.

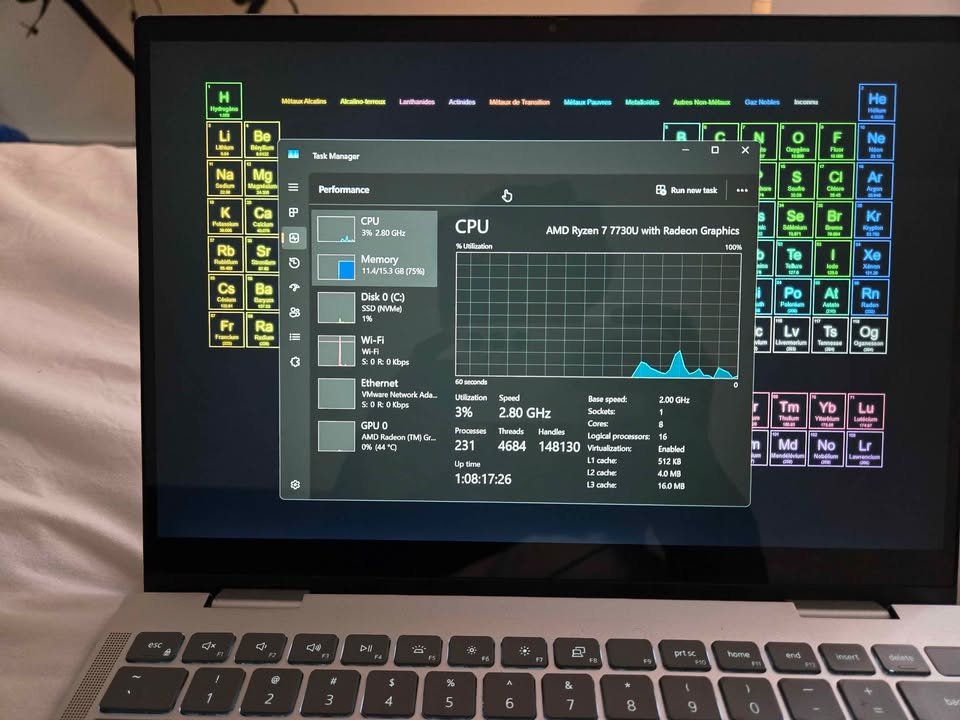
This processor is a 4 Performance-core 4 Efficient-core processor, which makes it 8 cores and 12 threads. It has a 45W base TDP, which means that it is more about sustained performance than battery efficiency.
The cores within the i5 13420H are used with different purposes. Performance-cores are used to process single-threaded tasks that are demanding and Efficient-cores are used to process background processes. The processor performs well under different workloads because they are intelligently synchronised with each other.
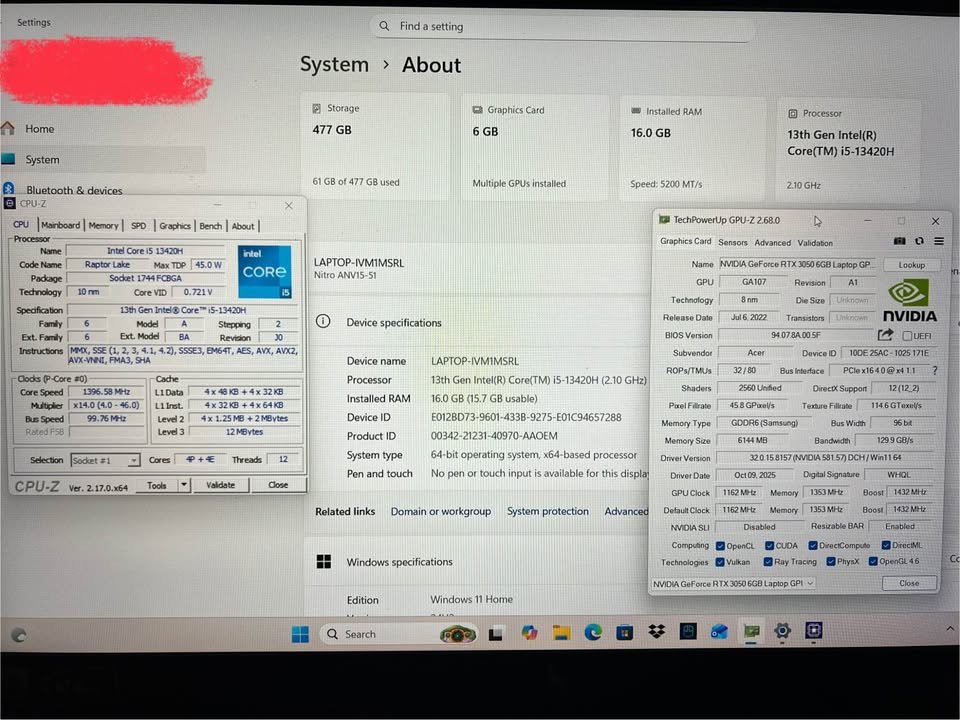
Note that both the core types, which are Performance and Efficient, are part of the total computing power. As a rule, Performance-cores have higher frequencies up to 4.6 GHz than Efficient-cores at 3.4 GHz. They are also more effective in intensive compilation. Nevertheless, they do not necessarily apply more to every coding situation.
The variations of the types of core are important in particular work. The most important thing is the way Intel Thread Director handles the distribution of workload. The final result will be impacted by any alterations in software optimisation and thermal conditions.
AMD Ryzen 7 7730U vs Intel Core i5 13420H: 10 Similarities and Differences
Both AMD and Intel processors are sufficiently good in terms of coding and programming. Nevertheless, the i5 13420H is stronger in prolonged working loads, whereas the Ryzen 7 7730U is more efficient in battery life. The trade-off is that the higher the performance, the less portability and battery life.
It is worthwhile to note that not all laptops are using these processors in the same manner before proceeding any further. Similarly, the actual performance among manufacturers differs.
And now we are going to compare and contrast AMD Ryzen 7 7730U and Intel Core i5 13420H:
#1. Core Count and Threading
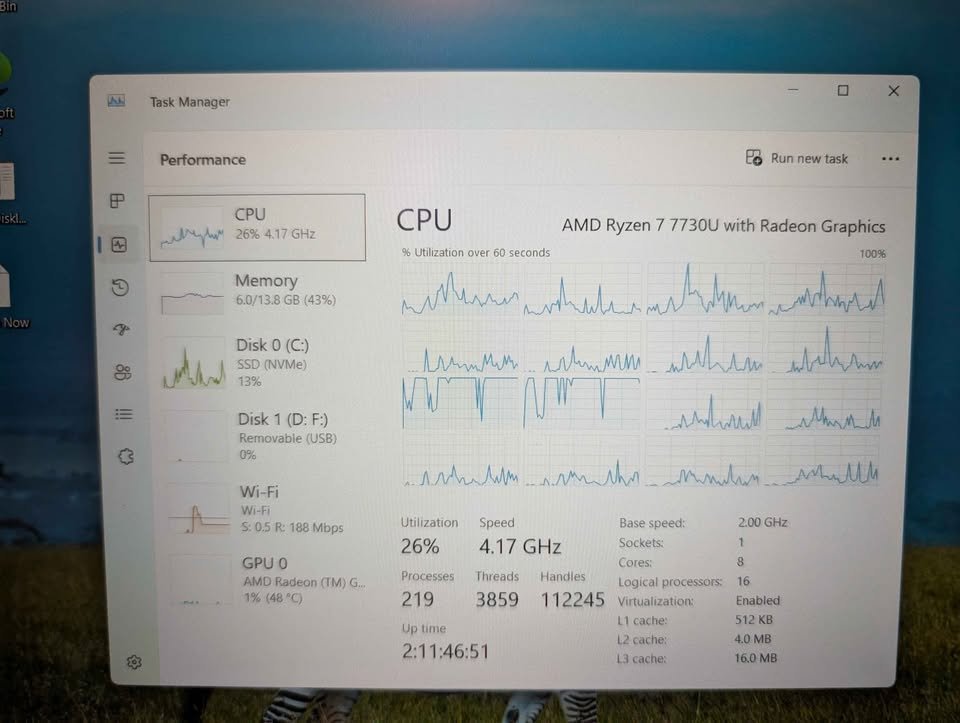
- AMD Ryzen 7 7730U has 8 cores with 16 threads with simultaneous multithreading (SMT). It has more threads than the other, so it is recommended to those who have numerous IDEs, containers, or virtual machines running at the same time.
- Intel Core i5 13420H has 8 cores with 12 threads with its hybrid architecture. Performance-cores by Intel provide very good results in many developers who care more about single-threaded compilation speed than the number of threads to use in parallel workloads.
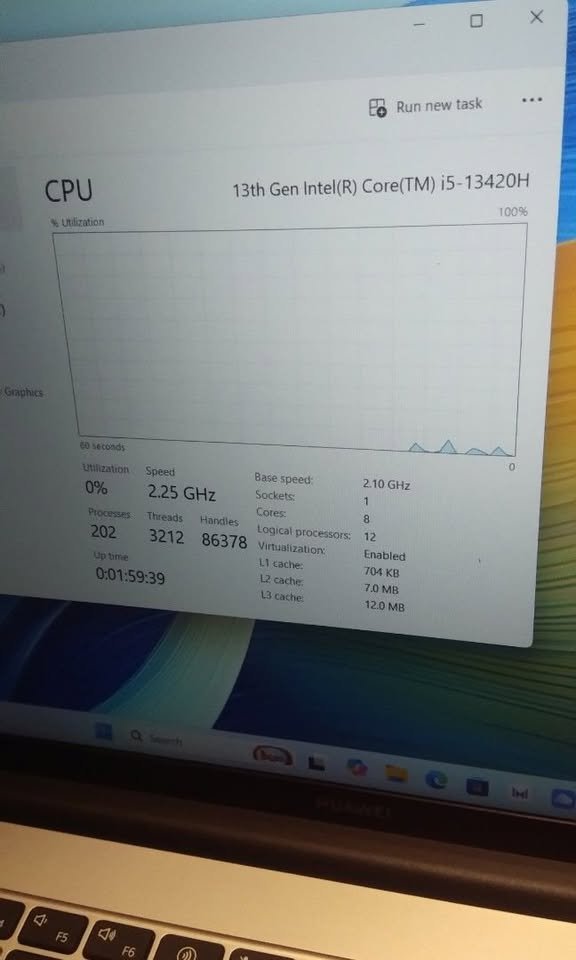
#2. Clock Speeds
- AMD Ryzen 7 7730U has a base clock of 2 GHz and a boost of 4.5 GHz. The lower base clock however indicates its efficiency-based design, which assists in sustaining longer battery life when performing light coding tasks. Cheque the impact on practical compilation times.
- Intel Core i5 13420H, which has a 45W TDP, has sustained higher clock speeds. As stated above, Performance-cores have 4.6 GHz whereas Efficient-cores have 3.4 GHz. This translates to faster code compilation, see how.
#3. Power Consumption
- Intel Core i5 13420H has the base TDP of 45W and the peak turbo power of 115W. This implies that it provides greater raw performance and consumes much more power. Our battery life comparison is below.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7730U, in its turn, has default TDP of only 15W. Ryzen processors are also efficient and can be used in portable development and therefore you will have a higher chance of coding longer hours without being at an outlet. Our efficiency analysis is below.
#4. Cache Architecture
- Although the two processors have multi-level cache systems, they vary in terms of L3 cache size. The AMD Ryzen 7 7730U has 16MB of L3 cache that assists in large codebases and high context switching. See the performance comparison of the cache below.
- Intel Core i5 13420H has 12MB Intel Smart Cache. To most programmers this is adequate to most programming tasks, but larger programmes might use the extra cache provided by AMD. The compilation benchmark results are presented below.
#5. Memory Support
- In the case of the Intel i5 13420H, you can have faster memory speeds of up to the DDR5 5200 MT/s or LPDDR5/x 5200 MT/s. When you are working with memory-intensive development environments, this offers performance improvements that can be felt. The same advantages are extended to the use of many virtual machines.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7730U, in its turn, has DDR4 memory that is characteristic of its laptop applications. On the one hand, it can lead to a slight decrease in memory bandwidth. Nevertheless, it also implies the ability to match it with cheaper laptop setups. This is not such a problem with most coding tasks, but with large datasets some developers might find the Intel memory support beneficial.
#6. Integrated Graphics
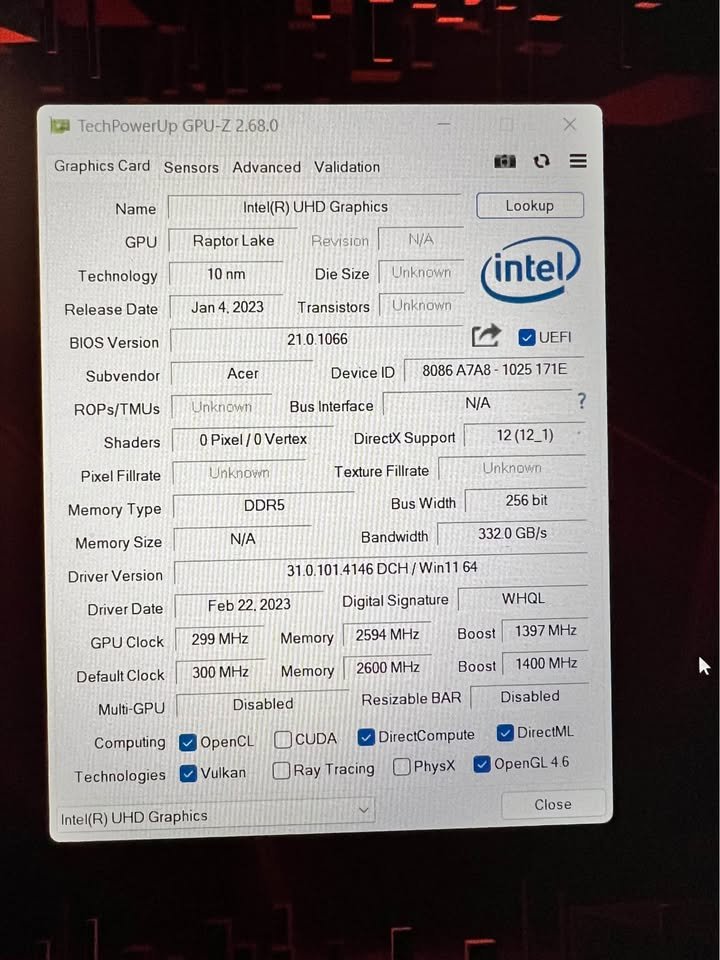
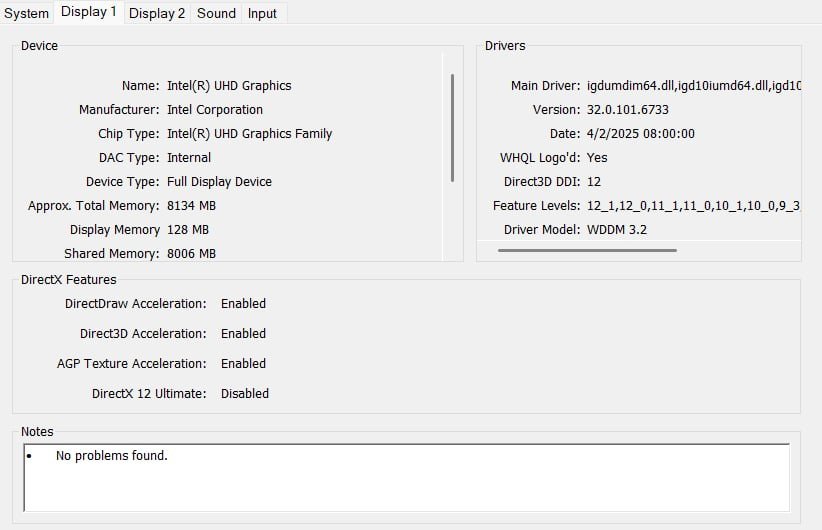
- Both AMD and Intel processors have inbuilt graphics that can be used in development. The exception one and the most important is the ones that require CUDA support of machine learning. A discrete graphics card is an alternative to a GPU-accelerated development in case you need it.
- As a rule, AMD Radeon Graphics of 8 compute units is a desirable option when working with OpenCL or Vulkan development. Besides, it also supports hardware-accelerated video encoding very well.
#7. Thermal Performance
- The Intel i5 13420H has an average operating temperature of up to 100 o C when loaded, which depends on the cooling design and the way the manufacturers apply it to the laptop. In case you are especially worried about thermals, look at laptops that have a solid cooling system.
- AMD Ryzen 7 7730U does not exceed 95 o C with proper cooling. With a laptop that is well thermally designed, then you may find that it operates quietly when you are on a long coding project.
#8. Platform Features
The current Intel processors tend to have sophisticated platform capabilities. Such features as Thunderbolt 4 support, which allows connecting external storage and display at high speeds, are included. They also endorse Intel Thread Director to manage intelligent workload.
AMD processors have their own benefits such as the improved support of Linux drivers and more stable performance across operating systems.
Intel has developed synthetic latex equivalents such as Intel security features such as TDT and VT-x but AMD has responded with AMD-V and equivalent virtualisation support.
The two platforms are compatible with key development features, although the implementation is different depending on the manufacturer of the laptop.
In case you are worried about compatibility with the platform, investigate your development needs.
Given your requirement of Thunderbolt connectivity and external GPUs.
You can also test performance of virtualisation to develop containers.
Preferably, select a laptop that has the connectivity and features that your workflow requires. The modern development is usually in need of quick storage and multiple display.
#9. Physical Implementation
In most cases, the laptops of Intel i5 13420H are thicker and heavier than the ultrabooks of Ryzen 7 7730U.
The average weight of a laptop is between 3 and 5 pounds depending on the size, construction, cooling design and so on.
By contrast, the laptops with Ryzen 7 7730U are as light as 2.5 pounds. The average development laptop is however approximately 3-4 pounds with a well furnished one.
It is worth mentioning that the increased TDP of Intel demands stronger cooling. Laptops can have bigger fans and heat pipes since they produce more heat.
#10. Software Compatibility
AMD processors are designed on the basis of x86-64 architecture, which is a popular instruction set. They are also usually very compatible with Linux as opposed to certain Intel specific features.
Both processors are compatible with all development environments. These products can be used with windows, Linux and containerised workflows.
Some compilers contain Intel-specific optimisations, which can favour the i5 13420H, although the difference is usually small.
The open-source driver support by AMD tends to be more out-of-box Linux friendly.
AMD vs Intel Core i5: Ryzen 7 7730U vs Intel Core i5 13420H: Our Verdict.
As you may observe, the two processors have advantages and disadvantages in terms of coding and programming. Developers are fond of the raw power and sustained performance offered by Intel hybrid architecture, and others of the better battery life and number of threads provided by the AMD platform with Ryzen.
We suggest AMD Ryzen 7 7730U to users who want a more portable development machine that has a high level of multi-threaded performance. Intel Core i5 13420H, in its turn, is faster in single-thread and has Thunderbolt 4 connectivity.
In battery life, AMD is much more efficient than Intel, and also less sustainable at high loads.
In both cases, you will be able to get great development laptops at different price ranges.
Having learned a bit more about AMD Ryzen 7 7730U vs Intel Core i5 13420H, it is time to make a choice. Take into account your development workflow, portability requirements and preferences and your budget.
In case you are still uncertain, you can use our tutorial on how to select a laptop to do programming, or you can get in touch with us to ask any questions that you might have.
FAQ
The strengths of AMD Ryzen 7 7730U and Intel Core i5 13420H are quite different hence what may suit one developer may not suit others. Intel is characterised as having superior single-thread performance and Thunderbolt whereas AMD is characterised by superior battery life and greater number of threads.



